Market Overview
Modern trends in network development have conflicting goals, the operator seeks to simplify data delivery to the user and transfer all resources to cloud services, thereby simplifying the intricacies of routing and avoiding a “bottle neck” in his network by prohibiting tunneled user traffic.
The user, in turn, also wants to reduce the increasing database at the expense of cloud services, but these services must be accessed through the use of various kinds of VPN connections.
The consequences of these contradictions are a decrease in the speed of information transfer, the presence of large unhelpful data overheads on the packets passing through the network, which leads to inefficient use of network bandwidth, a significant increase in network latency, lower quality of end-user service, etc.
The solutions offered by service providers do not always meet the stated conditions, or are not economically attractive. This is primarily due to the operator’s lack of tools to monitor and diagnose such solutions, as well as the degradation of the operator’s own networks, due to the inability to manage and control such solutions.
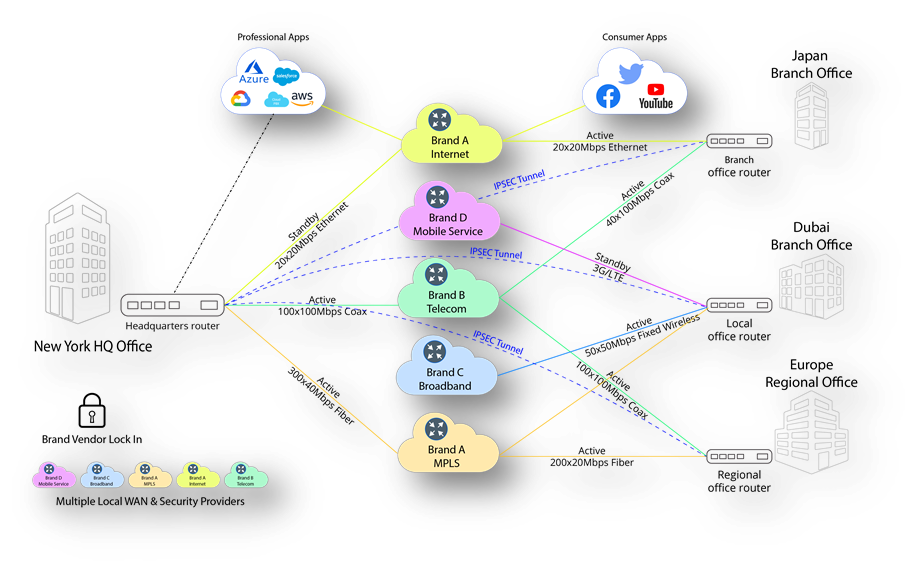
To overcome these contradictions, an approach to the design and deployment of a global enterprise network (SD-WAN), which uses software-defined networks (SDN) to find the most effective way to route and manage traffic, was proposed.
However, implementing this approach using legacy traditional data communications protocols has not yielded any meaningful results.
The use of SD-WAN solutions leads to an increase in power-consuming routing equipment at user sites, requiring the presence of qualified personnel, which in turn leads to user dependence not only on the operator or provider, but also on the manufacturer of the solution, the cost of equipment and the cost of training and staff maintenance, serving this solution.
A significant part of the corporate market is a solution based on MPLS. And today, despite the archaic, energy-intensive, expensive, MPLS solution remains dominant in the world.
In this case, modernization, expansion, optimization of production and maintenance costs of the network as a whole, becomes in fact a difficult task that requires long approvals, significant financial investments and as a consequence, a long time of implementation.
However, modern trends and economic circumstances occurring in the world require a global change in the network infrastructure not only in the corporate sector, but also in all sectors as a whole.
New economic conditions and trends that emerged in 2020 require operators to provide services to consumers not only at a completely different level of service quality, but also a different cost of implementation and energy consumption of services provided.
In this paradigm, not MPLS and even more so SD-WAN can not offer any rational solution.
Climate change in 2021 has shown the world that without the collation of operators, the provision of services to the corporate sector is virtually impossible.
And the provision of services based on MPLS does not meet any modern criteria.
One of the reasons is low environmental friendliness of such services.

Modern high-performance routers are made on “hot” platforms, in order to maximize the performance of routed traffic. In turn, to ensure operating modes, such routers require cooling and expensive maintenance by qualified specialists.
Accordingly, to install such equipment in each subdivision of the enterprise or an employee at home, firstly, expensive in terms of the cost of the equipment itself, and secondly, unprofitable in terms of the cost of maintenance and maintenance of the network as a whole.
To realize such needs, equipment on “cold” platforms is widely used. Such equipment does not require placement in cooled technical areas, has low power consumption and therefore lower performance. But, often, such implementations are incompatible with each other, or are not economically attractive, due to the use of outdated network solutions, protocols and design methods.
The use of archaic design methods originally created in the 1980s for “hot” X-86 platforms is long outdated for “hot” platforms and even more so cannot be used for any modern hardware platforms.
The architecture and design of modern technology solutions can not use protocols developed in the last century, designed to serve a small, low-performance market sector.
The use of any generation of IPSec protocols (commonly called VPN), leads to the inevitable degradation of any network, increased power consumption, and the lack of any security of the network, because it is a common program in the user space.
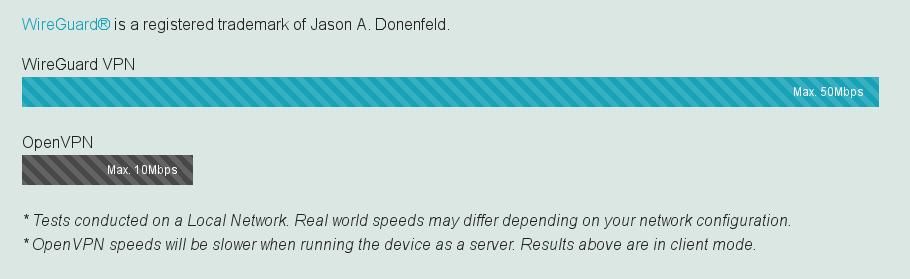
For example, I will give a comparative test of two recently developed data transfer protocols: OpenVPN, working in user space and WireGuard – not so long ago appeared in the Linux kernel, respectively working in the kernel.
The diagram shows that the performance of OpenVPN is 5 times less, in practice, this difference increases by up to 10 times. Accordingly, there is no serious business application of such VPN, due to the lack of security, reliability and any guaranteed performance.

The similar archaic solution includes the design of corporate services in the WAN, based on the third OSI model, which requires constant monitoring by qualified specialists and consumes a significant amount of router resources for the implementation of firewall tables, shapers, etc.
This design does not meet the current trends and requirements of not only the corporate sector, but also the requirements of private users.
In order to address the increasing demand for private networks, a family of tunneling protocols was created to organize VLANs over a UDP tunnel. There are 20 different UDP-based solutions used to support VLANs. One of the most common and widely used protocols is L2TP.
Although L2TP acts like a Layer 2 protocol in the OSI model, it is in fact a session layer (L5) protocol and uses a registered UDP port. Using such a solution requires high quality Internet channels on both sides of the tunnel and adversely affects the utilization of communication channels, as a rule such a solution can not have a performance higher than 25-35%.
Accordingly, all of the above technologies, protocols and solutions based on them do not meet modern requirements and are economically and environmentally unacceptable.
At the same time, communication and exchange of information at strategically important sites is possible only through the Internet and IP-technologies.
To create a modern energy-efficient productive network architecture and design for the consumer market, it is necessary to use modern diagnostic tools and control processes occurring in the network, both from the operator and from the user side.
Application of nuclear tunneling data transfer protocols, working on the second level of OSI model in the WAN, allowing to build a high-performance platform on a fundamentally new logical network architecture, and a new method of processing data packets, which can work with the existing physical channels and can guarantee the quality of services.
And it will also simplify routing setup in local networks, by segmenting traffic, centralizing management and monitoring of the network as a whole, and moving high-performance “hot” equipment to cloud resources.
This approach will ensure maximum security through the use of monolithic tunneling channels running from core to core at Layer 2 of the OSI model and reduce the possibility of DDoS and other IP-based network attacks.
It will reduce the load on the end-user equipment, which in turn will reduce the power consumption of the network as a whole and allow the efficient use of network resources and provide connectivity between the cloud, offices and users.

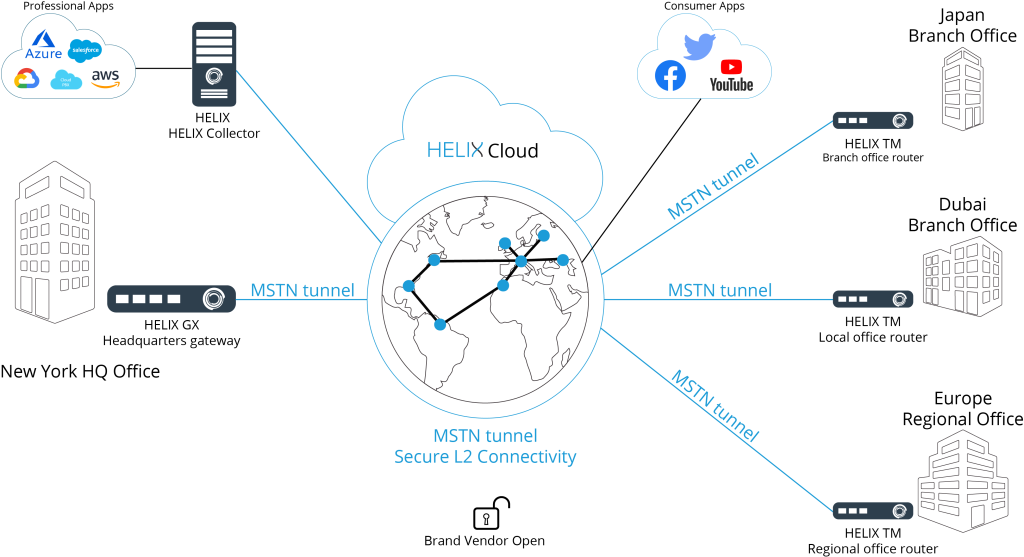
The HeliX networking platform, based on MSTN technology, has a turnkey solution to all of the above problems – the Autonomous Traffic Management System (AS), which enables rational use of network resources.
HeliX MSTNT platform is based on Multi-Platform Tunnel OS (MPT OS) operating system, which is installed on any modern telecommunications equipment, implemented on processors with X86, ARM, MIPS architecture. Which allows you to create a distributed corporate networks of different complexity and cost of implementation, but the same level of technological solutions and security.
The Autonomous System (AS) has all the necessary tools to manage and monitor, diagnose and control all processes occurring in the network, both from the user and from the operator or provider.
MSTN technology is developed using a completely new architecture that overcomes all existing shortcomings and limitations of traditional networking solutions.

